Bootstrap Breakpoints Grid
Introduction
Getting in idea all of the possible screen widths where our internet pages could eventually present it is important to form them in a method giving universal sharp and effective visual appeal-- commonly working with the assistance of a efficient responsive framework just like easily the most popular one-- the Bootstrap framework which latest version is now 4 alpha 6. But what it actually does to assist the pages show up terrific on any display screen-- let's check out and view.
The main concept in Bootstrap typically is placing some system in the unlimited possible gadget display sizes ( or else viewports) putting them in a number of variations and styling/rearranging the information appropriately. These are as well named grid tiers or display dimensions and have progressed quite a bit throughout the various versions of one of the most well-known lately responsive framework around-- Bootstrap 4. (see page)
The best way to use the Bootstrap Breakpoints Default:
Basically the media queries get determined with the following format
@media ( ~screen size condition ~) ~ styling rules to get applied if the condition is met ~min-width: 768pxmin-width: 768pxChanges of Bootstrap editions
Within Bootstrap 4 compared to its forerunner there are actually 5 screen sizes but given that recent alpha 6 build-- simply 4 media query groups-- we'll get back to this in just a sec. Considering that you most likely know a
.row.col -Display dimensions
The display screen dimensions in Bootstrap generally use the
min-widthExtra small – widths under 576px –This screen actually doesn't have a media query but the styling for it rather gets applied as a common rules getting overwritten by the queries for the widths above. What's also new in Bootstrap 4 alpha 6 is it actually doesn't use any size infix – so the column layout classes for this screen size get defined like
col-6Extra small-- sizes less than 576px-- This display screen in fact does not provide a media query though the designing for it rather gets used as a usual rules becoming overwritten by the queries for the sizes above. What is really also brand-new inside of Bootstrap 4 alpha 6 is it simply doesn't operate any sort of scale infix-- so the column layout classes for this particular display screen scale get defined just like
col-6Small screens-- employs
@media (min-width: 576px) ...-sm-.col-sm-6Medium displays-- applies
@media (min-width: 768px) ...-md-.col-md-6Large display screens - utilizes
@media (min-width: 992px) ...-lg-And finally-- extra-large display screens -
@media (min-width: 1200px) ...-xl-Responsive breakpoints
Given that Bootstrap is built to be mobile first, we employ a fistful of media queries to develop sensible breakpoints for formats and user interfaces . These types of Bootstrap Breakpoints Css are primarily built upon minimal viewport widths as well as let us to graduate up components while the viewport changes. (read this)
Bootstrap generally utilizes the following media query ranges-- or breakpoints-- in source Sass data for design, grid structure, and components.
// Extra small devices (portrait phones, less than 576px)
// No media query since this is the default in Bootstrap
// Small devices (landscape phones, 576px and up)
@media (min-width: 576px) ...
// Medium devices (tablets, 768px and up)
@media (min-width: 768px) ...
// Large devices (desktops, 992px and up)
@media (min-width: 992px) ...
// Extra large devices (large desktops, 1200px and up)
@media (min-width: 1200px) ...Given that we prepare resource CSS in Sass, all media queries are actually obtainable by Sass mixins:
@include media-breakpoint-up(xs) ...
@include media-breakpoint-up(sm) ...
@include media-breakpoint-up(md) ...
@include media-breakpoint-up(lg) ...
@include media-breakpoint-up(xl) ...
// Example usage:
@include media-breakpoint-up(sm)
.some-class
display: block;We occasionally apply media queries which move in the various other course (the delivered screen scale or even more compact):
// Extra small devices (portrait phones, less than 576px)
@media (max-width: 575px) ...
// Small devices (landscape phones, less than 768px)
@media (max-width: 767px) ...
// Medium devices (tablets, less than 992px)
@media (max-width: 991px) ...
// Large devices (desktops, less than 1200px)
@media (max-width: 1199px) ...
// Extra large devices (large desktops)
// No media query since the extra-large breakpoint has no upper bound on its widthAgain, these types of media queries are additionally accessible through Sass mixins:
@include media-breakpoint-down(xs) ...
@include media-breakpoint-down(sm) ...
@include media-breakpoint-down(md) ...
@include media-breakpoint-down(lg) ...There are likewise media queries and mixins for targeting a particular part of display screen dimensions employing the lowest and maximum Bootstrap Breakpoints Css sizes.
// Extra small devices (portrait phones, less than 576px)
@media (max-width: 575px) ...
// Small devices (landscape phones, 576px and up)
@media (min-width: 576px) and (max-width: 767px) ...
// Medium devices (tablets, 768px and up)
@media (min-width: 768px) and (max-width: 991px) ...
// Large devices (desktops, 992px and up)
@media (min-width: 992px) and (max-width: 1199px) ...
// Extra large devices (large desktops, 1200px and up)
@media (min-width: 1200px) ...These types of media queries are as well obtainable through Sass mixins:
@include media-breakpoint-only(xs) ...
@include media-breakpoint-only(sm) ...
@include media-breakpoint-only(md) ...
@include media-breakpoint-only(lg) ...
@include media-breakpoint-only(xl) ...Additionally, media queries can span multiple breakpoint sizes:
// Example
// Apply styles starting from medium devices and up to extra large devices
@media (min-width: 768px) and (max-width: 1199px) ...
<code/>
The Sass mixin for aim at the exact same display screen size range would certainly be:
<code>
@include media-breakpoint-between(md, xl) ...Conclusions
In addition to describing the size of the webpage's elements the media queries take place all around the Bootstrap framework commonly having defined by it
- ~screen size ~Inspect a number of online video guide relating to Bootstrap breakpoints:
Related topics:
Bootstrap breakpoints authoritative records

Bootstrap Breakpoints trouble
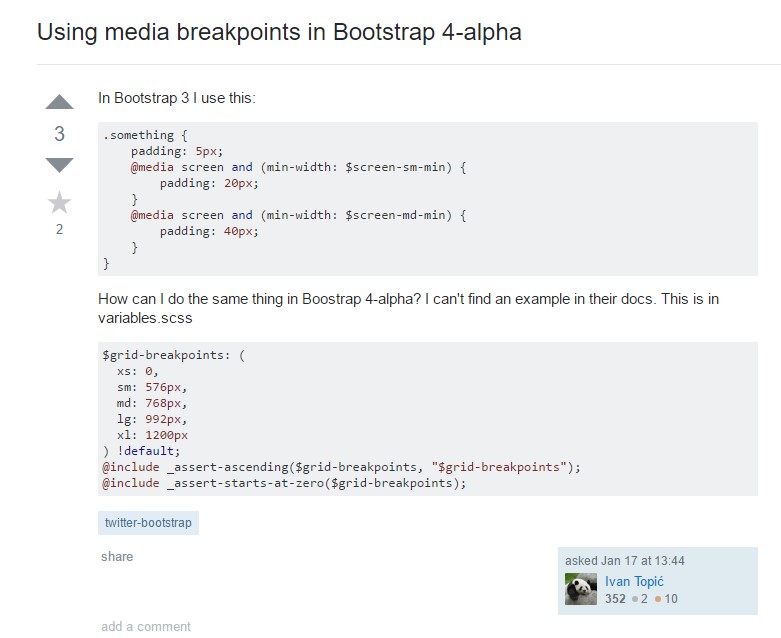
Transform media query breakpoint systems from 'em' to 'px'